modified tibial compression test|cranial cruciate rupture canine : importers This review identified that the McMurray's test is of limited clinical value due to relatively low sensitivity, with modified tests (associated with the traditional McMurray's test) having higher . Resultado da 30 de dez. de 2016 · AGROFIT. Compartilhe: Publicado em 30/12/2016 10h53 Atualizado em 21/05/2019 16h00. É um banco de informações sobre os produtos agroquímicos e afins registrados no Ministério da Agricultura. Permite a realização de pesquisas importantes para o controle de pragas .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da O Que Fazemos nas Sombras. . Na Mira do Júri. A MENINA QUE MATOU OS PAIS – A CONFISSÃO. Detalhes. Saiba mais. Classificação do conteúdo Nudez, violência, cenas assustadoras, uso de álcool, linguagem ofensiva, Conteúdo Sexual Legendas Indisponíveis
what is medial buttress
how hard is the vtne test
Objective: To assess diagnostic efficacy of a modified tibial compression test in predicting medial meniscal injury in dogs with cranial cruciate ligament failure. Objective. To assess diagnostic efficacy of a modified tibial compression test in predicting medial meniscal injury in dogs with cranial cruciate ligament failure.The Apley's grind test (Apley Compression test) is used to evaluate individuals for problems of the meniscus in the knee. This test is named after Alan Graham Appley (1914 - 1996), a British .A meticulous orthopedic examination should be performed with the patient under sedation to assess stifle instability using cranial drawer and tibial thrust, check for presence of meniscal .
This review identified that the McMurray's test is of limited clinical value due to relatively low sensitivity, with modified tests (associated with the traditional McMurray's test) having higher .
The Apley grind test, also known as the Apley compression test or the Apley test, is a maneuver performed to evaluate meniscus injury. Clinicians usually perform it in .This study investigated the diagnostic accuracy of 5 physical examination tests for predicting medial meniscal damage in cases of CCL failure. The tests, which were performed under .The McMurray test is a manipulative test used to diagnose meniscal tear in the knee. It involves rotating the tibia internally and externally while applying valgus stress and extending the knee. . To assess diagnostic efficacy of a modified tibial compression test in predicting medial meniscal injury in dogs with cranial cruciate ligament failure. Dogs admitted for surgical .
Introduction [edit | edit source]. Meniscus tears are the most common injury of the knee. Medial meniscus tears are generally seen more frequently than tears of the lateral meniscus, with a ratio of approximately 2:1. Meniscal tears may occur in acute knee injuries in younger patients or as part of a degenerative process in older individuals.
Definition/Description [edit | edit source]. The Noble’s test (Noble's Compression test) is a provocative test of the iliotibial band, developed by Clive Noble. It is commonly used as an indication for iliotibial band syndrome; however, no evidence-based research has been done yet to control the validity of this test.Other tests that could be used are the modified Ober’s test . Background: Cranial cruciate ligament (CCL) disease remains one of the most common hindlimb orthopaedic conditions seen in dogs, and although surgical management provides good outcomes, prevention remains the holy .After the modified TTA, the cranial drawer test was still positive in all dogs, whereas a negative tibial compression test was observed in nine stifles. The only stifle with a positive tibial compression test was determined to have a displacement of a lesser magnitude than after transection of the cranial cruciate ligament.
tibial thrust vs cranial drawer
Strain and Excursion of the Sciatic, Tibial, and Plantar Nerves during a Modified Straight Leg Raising Test Michel W. Coppieters,1,2 Ali M. Alshami,1 Awais S. Babri,3 Tina Souvlis,1 Vaughan Kippers,3 Paul W. Hodges1 1 Division of Physiotherapy, School of Health and Rehabilitation Sciences, The University of Queensland, QLD 4072 St. Lucia, Australia 2 Neuro Orthopaedic .included cranial drawer (in flexion and in extension), tibial compression test (TCT), modified TCT (mTCT), and stifle range of motion (ROM). Each dog was evaluated by a novice (one of 3 interns) and by an experienced clinician (one of 4 surgeons). Meniscal tears were confirmed via craniomedial arthrotomy and probing. A video demonstrating how to perform a tibial compression test (or tibial thrust test) in the canine patient. The tibial compression test (TCT) is a very useful diagnostic tool for identifying a torn Cranial Cruciate ligament in the dog. The TCT is also referred as .
The Straight Leg Raise (SLR) test is commonly used to identify disc pathology or nerve root irritation, as it mechanically stresses lumbosacral nerve roots. It also has specific importance in detecting disc herniation and neural compression.[2] [3][4]It is also classified as a neurodynamic evaluation test as it can detect excessive nerve root tension[5] or .
A small study supports the modified bent-knee test, with a LR+ of 10.2 and a LR– of 0.12. 17 In this test, the patient lies supine while the examiner lifts the leg to 90 degrees with the knee . Purpose The purpose of this study was to analyse the difference between arthroscopic fixation and open reduction internal fixation (ORIF) of posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) tibial avulsion fractures. Methods This retrospective study analysed patients with an acute PCL tibial avulsion fracture who underwent surgical treatment at our hospital and follow-up for .
The tests, which were performed under general anesthesia, included cranial drawer (in flexion and in extension), tibial compression test (TCT), modified TCT (mTCT), and stifle range of motion (ROM). Each dog was evaluated by a novice (one of 3 interns) and by an experienced clinician (one of 4 surgeons). Meniscal tears were confirmed via . The anterior drawer test evaluates the anterior cruciate ligament. When inserting an internal or external rotation to this test, anterolateral and anteromedial rotary instability can be evaluated. . Positive: Increased amount of anterior tibial translation with tibial internal rotation orAkseki et al 3 compared the McMurray's test with a weight-bearing version of the McMurray's test that incorporated axial compression and varus/valgus stress, with the patient squatting down in internal and then external rotation (Ege's test). The modified weight-bearing test showed a higher LR+ and a lower LR− than the McMurray's test (Table 7).Case history: Medical records from a single referral hospital (Animal Referral Hospital, Sinnamon Park, Australia) of dogs treated with modified triple tibial osteotomy (TTO) for management of cranial cruciate ligament (CrCL) disease from June 2017 to June 2020 were reviewed. Modifications to the originally described TTO procedure included a modified wedge angle .
Compression of the osteotomy was achieved, first, using bone holding forceps and, second, by placing the first and third distal screws in compression. Finally, tightness of all screws, range of movement, limb alignment, patellar . Create Personal Test Create Group Test . Tibial Plateau fractures are periarticular injuries of the proximal tibia frequently associated with soft tissue injury. . gentle mechanical compression on repaired .
The Femoral Nerve comes from the Lumbar plexus, see link.The femoral nerve lies within the femoral triangle which is bounded by the inguinal ligament (superiorly), the medial border of the Sartorius muscle and the lateral border of the Adductor Longus muscle (The muscles Pectineus and Iliacus and Psoas lie within this triangle as well). The femoral nerve lies (most laterally) .This video demonstrates how to perform the cranial drawer and tibial compression (tibial thrust) tests. This stifle is normal, and thus the tests are negative. In small-breed dogs with concurrent cranial cruciate ligament rupture (CCLR) and medial patellar luxation (MPL), correcting both disorders is are essential for restoring normal gait. However, the previously described surgical treatment, using two osteotomy technique, poses a high risk of fracture and instability. Addressing CCLR and MPL with a single osteotomy and . Lameness scores ranged from 0 to 1/10 (median, 0/10), cranial draw signs were present in all cases and the tibial compression test was positive in 50 stifles (91%). There was a significant increase in thigh circumference (P < 0.05) and a significant increase in stifle ROM (P < 0.05). There was no statistically significant increase in .
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome (TTS) is a mononeuropathy caused by compression of the posterior tibial nerve or its branches in the foot/ankle [1]. TTS is analogous to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, but occurs much more rarely, and usually as a result of trauma (fracture or sprain of the ankle), arthritis, or space-occupying lesions [2]. However, if the compression is located behind the patellar tendon, due to the small mobility of the patellar tendon, it is difficult to fully expose the fracture through a simple anterior internal or external incision 21 . Using the modified anterior median approach, a longitudinal incision is made on the lateral side of the tibial tubercle. In all cases, the tibial compression test was performed to confirm the absence of cranial tibial thrust. Once the wedge was in place, the flange of the plate was moulded, and a small area of the cranial tibial muscle was elevated so the flange could be inserted under it . A cranial drawer test or tibial compression test is used to evaluate craniocaudal instability of the stifle joint [7]. Recently, it was determined that the drawer test alone or combined with the .
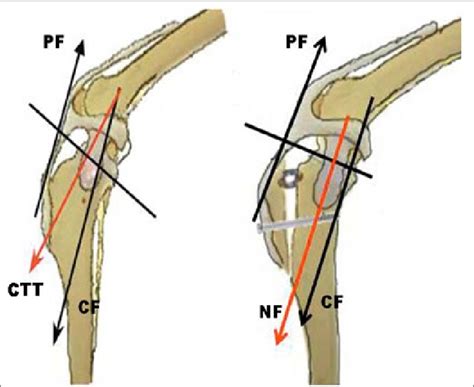
Veterinary Surgery, 2006. Objective— To evaluate the effect of tibial plateau leveling on the biomechanics of the canine stifle.Study Design— Analysis of a 3-dimensional (3-D) anatomically accurate theoretical model of the canine stifle.Methods— A 3-D, 3-segment mathematical model of the normal canine stifle was modified to simulate the effect of rotation of the tibial plateau . Objectives To evaluate long-term outcome using the BioMedtrix™ TPLO Curve® plate in dogs with cranial cruciate ligament disease (CrCLd) treated by tibial plateau leveling osteotomy (TPLO). Study design Retrospective case study. Animals Dogs (n = 323, 337 stifles). Methods Medical records were searched for dogs presented with CrCLd and treated by TPLO .
WEBGERAR. Confira os resultados do jogo do bicho da Paratodos Paraíba (PB) ao vivo. Números sorteados diariamente. Veja se a sorte está ao seu lado.
modified tibial compression test|cranial cruciate rupture canine